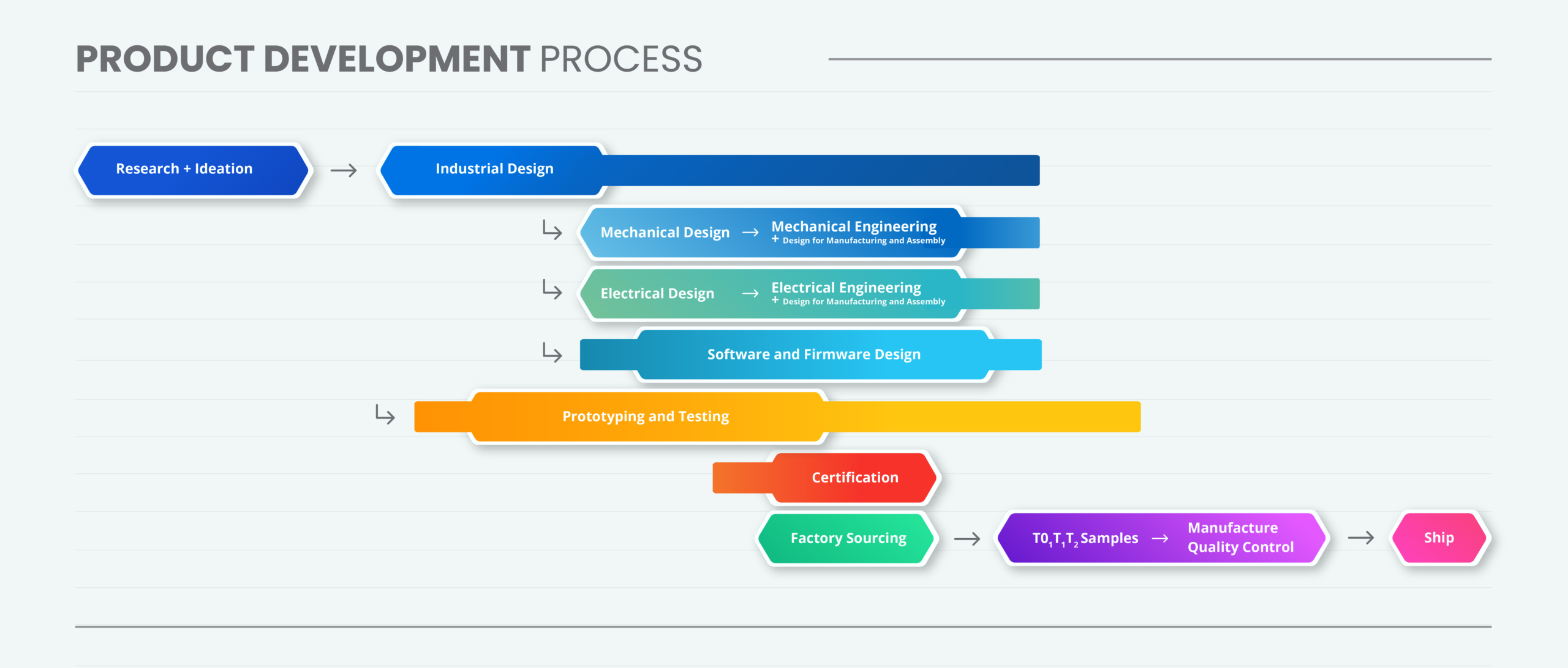
It happened – you had a light bulb moment – a product idea you know will be big – but how much will it cost to develop? The truth is, it depends on so many factors, it’s hard to say. But in this blog, we will look at the costs associated with developing a specific type of product – a physical, consumer product, made for mass production.
Although this is still an extremely broad category, we will take a look at the typical costs of each step in the product development process. We will dive into what determines the cost and why it varies depending on the type of product. Broadly speaking, the cost of product development will be from $60,000 to $175,000 and that can swing both high and low depending on who you hire, what you do yourself, the complexity of the project, and countless of other considerations.
Why so much? Well, there’s more to product development than meets the eye, and that’s what we’ll dig into today.
Let’s explore each of these potential costs and the factors that influence each cost:
- Why it’s important to know about each of these costs
- The Cost of Research and Ideation
- The Cost of Industrial Design
- The Cost of Technical Design (Mechanical, Electrical, Software)
- The Cost of Prototyping
- The Cost of Testing
- The Cost of Engineering (Mechanical, Electrical, Software)
- The Cost of Certification
- The Cost of Factory Sourcing and Set-up
- The Cost of Manufacturing Quality Control
- Bonus: The Cost of Shipping
There are also many soft costs, like finding and qualifying contractors, managing communications, timeline delays, etc., but today, we will focus on the more concrete aspects of the product development process.
Let’s dive in:
Why it’s important to understand product development costs before jumping in
There are many steps to the product development process, and each costs money – but not every step applies to every product in the same way.
Whether this is your first venture to creating a new product for the market, or you are a serial creator that has launched several products, knowing how much it would cost to develop your product is vital.
If you start blind, you may run out of funding before your product ever launches, disappoint investors, or show your naivety to strategic partners. In this article, we hope to give you insight into the process so you can start from a place of knowledge.
The Cost of Research and Ideation
[Cost: $2,500 – $5,000]
In planning to launch a new product, the first step is to understand the problem, and how you solve that problem. You want to see how big the problem really is and the greater market opportunity. There are many ways to do this, but the goal is to come up with a product concept with functional elements that serve as a foundation for product development.
With Research, a holistic and objective perspective of the problem is reached. This is often necessary because the founder of a business is intimately attached to the problem, and doesn’t always experience the problem the same way as everyone else. Although the founder is the one to finds the problem and often the solution, the product design process requires you understand these 2 things objectively so that they can be built not for the founder, but for the greater market need.
A product requirement document is often built at this stage to define what, exactly, is needed to define success. This works to mitigate scope creep throughout the design process.
Ideation (or idea formation) is the creative process of coming up with of potential ideas and solutions to the problems. There are many ways to go through this process, but generally, the outcome is a set of potential solutions to the problem or problems presented. The solutions can address a specific problem or all the problems. The chosen design is often some combination of multiple ideas.
What Determines the Cost of Research and Ideation?
It is very difficult to narrow down Research and Ideation as it is highly variable for different products. A few items that affect this range are:
- complexity of problem and solution
- background knowledge on the subject area
- what level of detail you are looking for
The Cost of Industrial Design
[Estimate: $2,500 – $10,000]
Industrial Design addresses how the product will look and feel in the product-human interaction, which determines who this product will sell to on the market.
Industrial Design considers every aspect of the product from appearance to functionality with the goal of creating a design that resonates with the customer and is intuitive to use. If you have ever picked up a product and it simply “made sense,” without reading the instructions, that is good industrial design.
This work is front heavy with sketching and modeling the product concept – “bringing the concept to life.” However, industrial design is important throughout the whole development process to ensure the design does not change or deviate heavily from the original solution. This is often a challenge during the later stages of development as the initial design must adapt to the functionality, reliability, and manufacturability of the engineering and production stages.
What Determines the Cost of Industrial Design?
This depends on how important design is for your product – many products will focus on function, while others will look to distinguish themselves through market positioning. Sometimes, you can adopt an existing product design that works just fine, but for novel products, this is often not the case. Considerations for this cost will include:
- the importance and value you put on the industrial design
- complexity of product
- number of use cases you are considering for the product
- whether designers and founder align on design and vision
The Cost of Technical Design
[Estimate: $15,000 – $30,000]
Technical design breaks down the ideas in the industrial design stage into feasible mechanical, electronic, and software systems. These systems are created using low volume, prototype-style design tools as a proof of concept. These designs are then iterated on to solve subsequent design challenges.
The purpose of this step is to make sure the functionality (or the aesthetic) of a product concept is feasible.
The technical design step happens in cycles with prototyping and testing. Systems are designed, prototyped, and tested. These cycles are repeated to address and overcome design challenges as well as roadblocks that come up throughout the design process.
Technical Design Cost Factors
Depending on the nature of the product, this stage can be extensive or relatively short. Complex projects will require many design iterations, while some products may be purely mechanical and can completely skip the electrical and firmware/software side of things.
It is difficult to estimate the time and cost associated with this stage and it is iterative and new challenges will often arise throughout the design process.
The Cost of Prototyping
[Estimate: $5,000 – $10,000]
Prototyping is about building a design so it can be tested.
Early on, this happens as part of the technical design cycle (design, prototype, test) where you are able to validate feasibility and address big risks. Later on, this happens as part of the engineering design cycle (engineer, prototype, test) where you validate engineering analysis, reliability concerns, and other more nuanced aspects of the design.
With the emergency of additive manufacturing (mainly 3d printers), prototyping has moved into earlier and earlier stages of the product development process, getting cheaper and cheaper. Learn more in our article, Prototyping in Product Development Today.
Factors Affecting Prototyping Costs
Prototyping starts at the early stages and ends in the late stages of the development process. It can be very cheap and quick for low fidelity functional prototypes and very expensive for high fidelity functional and aesthetic prototypes.
In general costs are also affected by
- Complexity of the prototype (number of parts, tolerances, mechanical integrity, etc.)
- Fidelity of the prototype
- Method of manufacture, materials, etc.
The Cost of Testing
[Estimate: $5,000 – $10,000]
Testing happens throughout the product development process. It happens in conjunction with prototyping as part of the design iterations.
Testing allows the design team to gather feedback on your designs. It helps the team to identify potential issues or validate product decisions. Testing also allows you to de-risk the product launch: by testing throughout the development of the product, the design team has constant feedback on what works and what doesn’t.
Product requirements should be clearly defined at this stage so that a prototype may be effectively evaluated on whether its performance is acceptable or not. Learn more in our article, Your Complete Guide to Product Testing.
Factors Affecting Testing Costs
Product testing costs vary depending on the product concept being tested:
- Riskier projects may require more testing and iterations to improve confidence and reduce risk
- If multiple product concepts are to be pursued, this will mean testing multiple concepts in parallel
- The less uncertainty you are willing to put up within the product testing outcomes, the more thorough your testing needs to be and the more it will cost
- Specific tests will require specific equipment
The Cost of Engineering
[Estimate: $25,000 – $50,000]
As the product goes through more and more detailed testing and refinements, engineering analysis is done to prepare for reliability, production, and regulatory requirements. Mechanical, electrical, software and firmware systems are optimized for cost, durability, efficiency, and other product requirements.
The focus at this stage is on getting the product design ready for mass production.
The product design is engineered to meet the initial specifications. Design requirements are reviewed, and analysis performed. Testing is carried out to validate calculations and ensure certification testing will succeed.
A lot of finer details are taken care of at this stage such as creating the quality control requirements, building the instruction manuals, and setting up for certification.
Cost Factors Affecting Product Engineering
- Number of parts and assemblies
- Safety devices, medical devices,
- High intensity environmental conditions
- Electrical and firmware/software systems
- External device integration
- Rare or complex materials and manufacturing processes
- High performance equipment
- Products requiring electrical hardware and software/firmware integration may cost more to create than the simpler ones
The Cost of Certification
[Estimate: $5,000 – $10,000]
Once the product prototype passes through internal testing to ensure that it is safe, reliable, and can meet its desired product specifications, it then needs to go through 3rd party product testing for certification, before it can proceed to mass production.
Product certification cost and timeframe is based on which certifications you choose to get and where you choose to get them.
Product certification is the process by which your product is tested to meet regulatory standards in a specific market or industry. For example, if you were selling a medical device, a safety device, or a wireless device, you would need to certify your product before selling it to consumers.
Types of product certifications can include:
- FCC certification, for all electrical products sold in the United States, although this certification is significantly more expensive for wireless products.
- UL certification or CSA certification, for any electrical product sold in the United States and/or Canada that plugs into an electrical outlet.
- CE certification, for most electronics sold in the European Union. This certification is like the FCC and UL certifications required in the United States.
- RoHS certification ensures that the product is free of lead and is required for products sold in the European Union or California.
Learn more about what certifications you need for your product at our blog: What Certifications are Needed for My product.
The Cost of Factory Sourcing and Set-up
[Estimate: $2,500 – $50,000]
Setting up for mass production can be a significant expense when developing a new product. This stage includes finding and qualifying the best manufacturing partner(s) for your product. Then, negotiating contracts (costs, timelines, quality control procedures, etc.) and setting up the production tooling.
After the final engineering design is complete, the final prototype (sometimes called the Golden Prototype) for production is prepared. The final drawing packages as well as this golden prototype will be used to set up production tooling and run t0, t1, and t2 samples. These samples are the first units created by the mass production tooling and allow you to refine how the end product will turn out.
Factors Affecting the Cost of Factory Sourcing and Set-up
There’s a lot that can define the cost of this step.
- The manufacturing process used (plastic molds are often the big cost at this stage)
- The complexity of your product and whether you will need to coordinate multiple factories or just one
- How specific you are with cost
- The production run quantities you will be making (and minimum order quantities)
- If the factory has made a similar product or if they have similar capabilities (vs making tooling from scratch)
- Manufacturing process used (is it manual, highly automated, how long it takes, etc.)
- Availability of materials
Learn more in our related articles, A Beginner’s Guide to Incoterms and The Price of Mass Producing Plastic Products.
The Cost of Manufacturing Quality Control
[Estimate: 0.5-2% of production cost. Often about $500 – $1,000 on a first order.]
Ensuring the quality of the product is absolutely essential. Quality control happens throughout the manufacturing process at the component level, the assembly level, and the final package level.
In the engineering stage, you will have identified a number of likely issues that need to be monitored in a quality defect document. You will work with the factory to roll out quality control checks throughout production line; however, it is important to also have a third party quality control partner to ensure this is done properly.
By checking often and throughout the process, you are able to find and address issues early on, saving considerable time and money.
Cost Factors Affecting Manufacturing QA
The cost of manufacturing quality control is affected by the scale of your order and the acceptable quality limit (AQL) you’ve chosen for your product. Learn more about acceptable quality limits at this article by QualityInspection.org.
Bonus: The Cost of Shipping
Although this article is focused on the product development costs, we will leave this here as an honorable mention as it is a significant cost. (Please note, this list also excludes the cost of the factory production order itself).
[Estimate: $1,500 – $25,000 (pre-pandemic to mid-pandemic for a 40’ container – China to North America)]
After production, it is important to ensure that your product gets to its destination safely. There are different ways to transport your product – if manufacturing in China, the two options are sea freight or air freight. Although this is the major differentiator, this stage refers to transportation from factory to fulfillment center.
This includes trucking from factory to port, export management, import management, trucking from port to train station, train transport, and trucking from train to fulfillment center. This is commonly referred to logistics, because there are many moving parts that need to be coordinated to execute this efficiently.
Factors Affecting the Costs of Shipping and Logistics
Air freight is a good option for small, low weight, high value products or when time is critical, but we will focus on sea freight as that is the more common path. The quantity of your order will determine the size and number of shipping containers you will use, but there are many nuances to this cost.
- The size of your package determines how many units will fit in a container and the corresponding cost/unit.
- Location of factory with respect to the port
- Palletizing your product (fit less product, pay for pallets, pay for forklift)
- Not palletizing your product (fit more product, pay more for manual loading and unloading, unloading delays and storage)
- Whether your shipping route is well travelled (lower cost, higher chance of delays)
- The type of product you are shipping (export and import duties)
- Additional shipping services like tracking and insurance
Estimate the cost of your freight with this FreightOS calculator.
Estimate the cost of import duties with this FreightOS calculator.
When diving deep, don’t trust the calculator, look for yourself using this US government database.
Conclusion
As you now know, product development is a complex process that is different for every project.
There are many steps and costs associated with the product development process. A ball park range for consumer products made for mass manufacture is $75,000 – $100,000 for professional, relatively simple product designs, plus extra for production and logistics.
However, these projects can quickly run over budget because from design issues, scope creep, and improper planning. Product development requires a great deal of communication and timeline management which is why full service product design firms are so convenient.
If you want to know more about product development and how to bring your product from concept to market, learn more about The Ventrify Design Process Here or check out our other insights.
About the Author
Ventrify is a product design and manufacturing firm that helps entrepreneurs bring product ideas from concept to market. We take in fledgling ideas and bring them through our iterative design process to create products our clients can be proud of. Then, we work with manufacturing facilities worldwide to bring our clients the highest quality products at competitive prices.
If you have questions about estimating the cost of your product development or need help, reach out to us through our Website, Facebook, or LinkedIn.